Evaporative Cooling
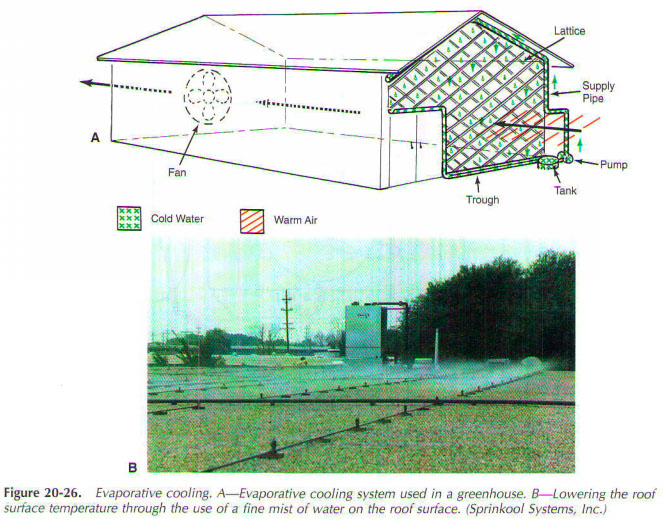
Evaporative cooling is often used in climates with bright sunshine and low relative humidity. For example, evaporative cooling can maintain a safe temperature for growing plants in greenhouses. One end of the greenhouse has a grid of fibers, such as excelsior (fine, curled, sawdust). Water pipes in the small holes in the top of the lattice. Water from the small holes flows down, wetting fibers. Fan at the other end of greenhouse draws air through the lattice. The air is discharged to the outdoors.
Air entering the greenhouse will be cooler than the outside air. This is due to the evaporation of water on the surface of the lattice. Plants do best in conditions of high relative humidity. Thus, this type of cooling is ideal. It provides a high relative air humidity, as well as lower the temperature inside the greenhouse. Foundries, sometimes the use of this system in situations where several degrees cooling desirable. In such installations, evaporation occurs in the structure on the roof of the building. The cooled air descends into the workspace.
Shallow pool of water on the flat roof can be used for cooling purposes.
This pool will be 2" or 3" (50 mm and 75 mm in depth. Where the bright sun most of the day, building heat load can be high. If the relative humidity is generally low, ponded roof will maintain a comfortable temperature in the room.
Wet roof cooling sometimes referred to as "the marsh cooling". This method is used mainly when the temperature of ambient air temperature and high relative humidity is low. There are many methods of wet roof cooling. Some systems are designed so that the roof is a trough or a pond. The whole surface is wet and the water is replaced as soon as it changes phase.
Another method is to spray from the roof of the small drops of water. Roof spray is based on the fact that the water will change its state when sprayed on a hot tin roof. In doing so, it absorbs quite a large amount of heat from the surface of the roof. Evaporation continues as long as the temperature of the surface of the roof is greater than the ambient temperature wet bulb temperature, This will reduce the influx of heat through the roof. Surface temperature varies, depending on latitude, month, etc.
Various controls in the system of monitoring the temperature of the surface of the roof. They control the amount of water that is sprayed. It evaporates from the roof in accordance with the temperature at that time. The amount of water used is coordinated from the roof of the temperature and the ambient temperature. This allows the water to evaporate without overflow or stagnation.
The higher the temperature, the greater the amount of water vapor that may exist with the air in the atmosphere at any relative humidity. Evaporation will continue even when the relative humidity is 100%. As the heat source (the roof), which is in contact with water should be higher than the damp air/steam combination adjacent to the surface. The roof of the cooling system must support the roof surface temperature close to the wet-bulb, thus minimizes the heat flux through the roof.
Evaporative roof cooling can be used as a single system or as part of the mechanical air conditioning system or energy management program.
 .. ..
|

 ..
..