This condensation process
Superheated steam refrigerant enters the capacitor where it loses heat, passing by (i.e. the thickness of the tube wall) coolant. Coolant can be air or water or other liquids. The refrigerant vapour is first cooled its saturation temperature (depending on the steam pressure.), then condensation begins. As it condenses to a liquid at a constant temperature, the release of latent heat. Only when the condensation process is over, the refrigerant temperature began to fall again. This is cooled to a temperature below the condensation called hypothermia and is most often found in the liquid line. Condensation process is shown in Fig. 18. Fig. 19 and 20 show how the changes in the refrigerant temperature and coolant.
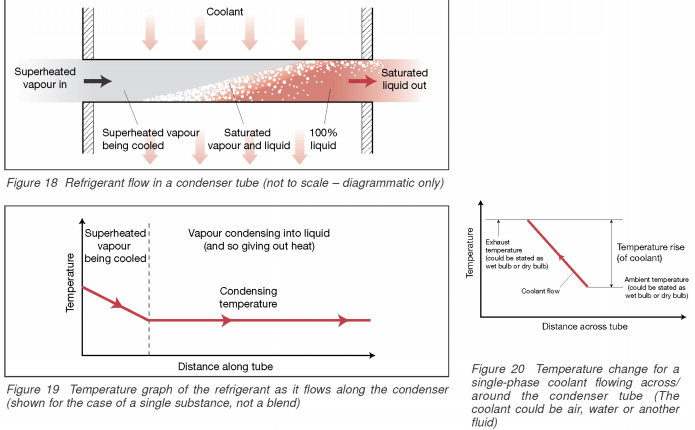
In the case of evaporative condensers the cooling effect is enhanced, allowing the water to evaporate into the air, passed over the pipes. This cools the air to cook bulb. This would give a slightly different coolant temperature schedule that shown in Fig. 20.
..
|

