The ideal cycle
Suitable reverse cycle based on two temperatures in Example 1.1 may be levied on the temperature and entropy basis (see Fig. 2.1).
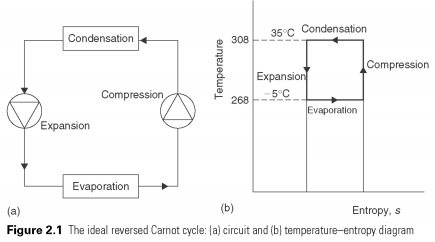
In this cycle of a unit mass of fluid is subjected to four processes, after which it returns to its original state. Compression and expansion processes shown as vertical lines, will take place in constant entropy. Constant entropy (isentropic) process is reversible or an ideal process. Ideal expansion and compression engines defined in Section 1.2. The criterion of perfection that is not entropy is created during the process, i.e., the number of 's' remains constant. Adding and refusal of heat takes place at a constant temperature, and these processes are shown as a horizontal line.
The work is transferred to the system during compression and from the system during expansion. Heat is transferred through the boundaries of a system at constant temperatures during evaporation and condensation. In this cycle the net quantities of work in the heat and proportions ensuring the maximum amount for cooling the minimal amount of work. The ratio efficiency of Carnot).
This cycle is called reverse the Carnot cycle, because the original concept was a heat engine, and the energy cycle of works in the direction of clockwise, generating net work.....
|

