Capacitors
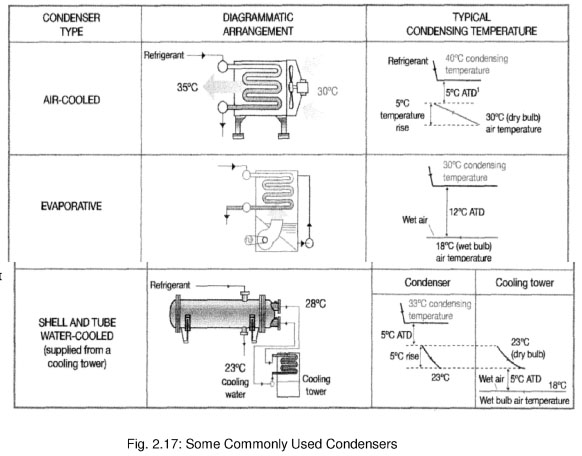
Condenser heat exchanger, where the refrigerant gas condenses giving up its heat to the atmosphere. Capacitors can be a natural draught cooling for small appliances, such as refrigerators, forced draught and condensers, air cooled, water cooled shell and tube condensers or water cooling plate heat exchangers or evaporative condensers. Some commonly used capacitors are shown in Fig. 2.17. In the case of water-cooled condensers, the water tends to be cooled in cooling towers or spray ponds. In some cases, evaporative condensers are used where water is sprayed on the coils, heat directly dissipates into the atmosphere, eliminating the need for separate cooling tower or spray pond.
Heat transfer coefficients in the range from 1400 up to 11000 W/m2K, depending on capacitor design and refrigerant used. Various question-types of heat exchangers in section 2.2.4 also relevant for condensers.
The majority of refrigerants have low surface tension, which promotes the formation of a thin film condensation on the external profile of the pipe.
Heat transfer is the inverse function of the thickness of a film of condensate and thus increases with a thin film of condensate. Therefore, short, vertical plates on a horizontal pipe gave smaller thickness of the film is typical of the tube.
An integral externally finned tubes, creation of longitudinally or spirally grooves and ridges in the fin tubes and other create turbulence and replenishment of water side heat transfer. These features contribute to the turbulence and may help slow the negative impact of fouling. However, finned tubes can save condensate, limiting its performance. Several extended surfaces with complex surface geometry were designed to foster surface tension-drain condensate.
Air cooled condensers, being limited to a dry bulb air temperature, as a rule, result in higher condensation of the refrigerant pressure and temperature, as compared with water cooled condensers, leading to higher compression ratios and higher power consumption (about 20% or above) in compressors. However, water shortages and a lack of treatment facilities, forcing many users prefer to air cooled condensers. In such cases, providing evaporative cooling pads before the capacitor can help reduce the condensing temperature and pressure when the weather is dry i.e. low humidity conditions.
Air cooled condensers to facilitate the use of hot air for heating in cold season.
- Capacitor improves performance when the fluid (air or water), the temperature is low.
- Evaporative condensers are more effective than the shell and tube condensers. However, it is difficult to recover in case of a puncture tube. Evaporative condensers are also more prone to corrosion due to the constant presence of air around the pipe.
The overall coefficient of heat transfer in heat exchanger is determined by the constructor and an application engineer has no control over it. When comparing heat exchangers, for the same duty conditions, the heat exchanger with the primary tube surface area will ensure a more efficient heat, other things being equal...
|

