Heat Pipes
Heat pipes have excellent heat-capacity, fast heat transfer speed, temperature distribution, simplicity of design, compactness, high reliability, high efficiency, low heat loss, low manufacturing cost, ecologically clean nature and generic applications. Their most attractive feature is that they do not require external sources of energy.
The concept of passive two-phase heat transfer devices capable of transmitting large quantities of heat with a minimum temperature difference was first introduced Gaugler in 1942. This device was paid little attention until 1964, when Grover and his colleagues from Los Alamos National Laboratory, published the results of an independent investigation and first used the term " heat pipe. Since that time, heat pipes have been used in many applications, ranging from the control of the temperature of the permafrost layer under the Alaska pipeline for thermal control of optical surfaces in space vehicles.
A heat pipe is a heat exchange device with extremely high effective thermal conductivity. Heat pipe evacuated courts, as a rule, circular in cross-section, which are made with a small amount of working fluid.
They totally passive and are used to transfer heat from the heat source to the heat sink with the minimum temperature gradients or isothermalize surfaces.
Heat pipes, as a rule, consists of a sealed container with a wicking material. Container evacuated and filled with just enough liquid to fully satisfy the wick. As shown in Fig. 7.1, the heat pipe consists of three distinct regions: the evaporator or heat addition region container, condenser, or heat the region, and the adiabatic or isothermal region. If the evaporator region is exposed to high temperature, heat is added and the working fluid moisture in the structure is heated until it evaporates. High temperature and corresponding high pressure in this area raise steam in the cooler condenser region, where the steam condenses, giving up its latent heat of vaporization. The capillary forces existing in wicking structure, and then pump fluid back into the evaporator. The wick structure, thus, ensures that the heat pipes can transfer of thermal energy in cases, if the heat source is cooled below the end (at the bottom of the thermal mode) or if it is above the cooled end (top-thermal mode).
A heat pipe is a synergistic engineering structure, which, under certain restrictions on the manner of use, equivalent material having a thermal conductivity is much higher that any known metal. Figure 7.2 is a cutaway view of a cylindrical heat pipe with homogeneous screen wick. The working liquid in the evaporator section and flows in the direction of the condenser section where it deposits its heat of condensation. The capillary forces in porous wick return of a shorter working liquid in the evaporator section. Heat transfer occurs through capillary movement of fluids. "Pumping" under the influence of forces of a superficial tension may be enough to move.
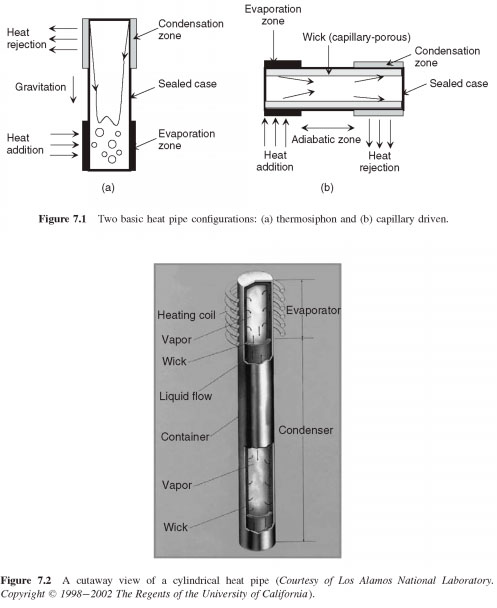
A heat pipe is a synergistic engineering structure, which, under certain restrictions on the manner of use, equivalent material having a thermal conductivity is much higher that any known metal. Figure 7.2 is a cutaway view of a cylindrical heat pipe with homogeneous screen wick. The working liquid in the evaporator section and flows in the direction of the condenser section where it deposits its heat of condensation. The capillary forces in porous wick return of a shorter working liquid in the evaporator section. Heat transfer occurs through capillary movement of fluids. "Pumping" under the influence of forces of a superficial tension may be sufficient for the movement of fluid from low temperature to high temperature zone (with their subsequent return in the form of steam, using as a driving force for the difference in the vapour pressure at two temperatures). Such a closed system, requiring no external pumps, which may be of particular interest in space nuclear reactors in the passage of heat from the reactor core to the radiating system. In the absence of gravity, the force must be only such as is overcome capillary and drag the return of steam through their channels.
Please note that the heat pipe Assembly, coil support and the induction coil gathered together as one, and they do not rotate. Instead, only the outer shell, or jacket, turns severe internal bearings mounted on each end of a nonrotating coil rod. This design eliminates the need for rotating units. When AC voltage of industrial frequency arrives, induction coil generates a flow lines, the direction of which alternate with the mains frequency. And, since the roll shell is mounted on the same axis as the induction coil, the shell function as one complete turnover of the secondary coil. Therefore, the coil, which receives power, heat, but rather, shell heats up, after Faraday's law. Thus, roll shell itself is a source of heat, not to a remotely located heater or boiler. It is well known that the method of electromagnetic induction almost 100% efficient at converting electrical energy into heat. Shell has several gun drilled holes on the whole width of the roll is called jacket cameras, the number of which will depend on the roll specifications. In each of the chambers, a small amount of coolant is placed, then, in each cell seal and evacuated. So, we have cooled in a vacuum.
When the roll is operating, the heat from the induction principle reasons for this cooled to evaporate. Because the steam pressure more than the pressure of condensation of vapors should move to any cooler jacket camera, then condenses, giving to the surface of the shell is the latent heat of vaporization. Thus, there is a continuous cycle of evaporation and condensation occurring in a vacuum of each jacket chamber in which this phenomenon, known as the principle of a heat pipe. These heat pipes have extremely high rates of heat transfer (almost the speed of sound) and each heat pipe contains a very large amount of latent heat. A heat pipe act is something that supports high accuracy of the roll surface temperature, because it reacts quickly and automatically, and any slight changes in heat load.
So, with temperature correction devices, precise surface temperature is maintained not only in the transverse direction, but in the longitudinal direction. As the oil flows through the logs of the rolls, the temperature of the log where the carrying beyond connection, about half of the roll surface temperature. This means that the outer bearings should last much longer and that high temperature bearings are not always needed. So, without rotary joints, no stamps, no oil leaks, and cooler running bearings, maintenance rolls markedly and is much less than ordinary rolls. More importantly, the environmental problems usually associated with oil and heat rolls eliminated...
|

