Direct expansion systems
Figure 10-7 shows the high temperature of your system [above 32F (0C)]drip-pan defrosting. In the course of a normal cycle cooling thermostat, the room temperature may rise above the thermostat setting. This indicates a need for cooling. Liquid solenoid (valve), pilot solenoid (valve B)and double-pressure valve D) open, allowing the flow of refrigerant. When the solenoid (valve D) is live. Low pressure hood adjust the control knob. The controller supports a given suction pressure in the evaporator. When the room temperature reaches the low setting on the thermostat, there was no need for refrigeration. At this time, solenoid valve and solenoid valve D close and remain closed until further cooling is needed. Hot gas solenoid (valve C) remains closed during the normal cycle cooling. When three-position selector switch is enabled Defrost, liquid solenoid valve and D, with integrated pilot solenoid close. This allows the valve D function as defrost pressure regulator high value. The hot gas solenoid (valve C) offer to provide the hot gas to enter the evaporator.
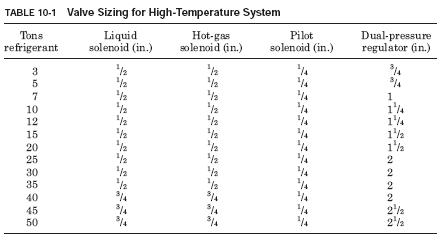
In the process of defrosting is complete, the system switches back to the normal cooling cycle. The system can be fully automatic, replacing the manual switch with electric time. Table 10-1 shows the dimensions of the valves needed for this system. 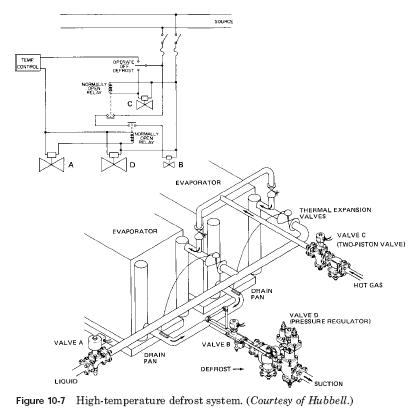
..
|


