Transcritical carbon dioxide cycle
Low critical temperature for carbon dioxide can be seen in the pressure-enthalpy diagram (Fig. 2.11) . Loop heat transfer at 31C would significantly lower the cooling effect than one condensation, say, 27C. Above the critical point, the gas cannot be accepted and must move in this region, if the temperature of the heat approaches 30C. If the gas is cooled by, say, 40C, as shown in Fig. 2.11, the cooling effect is the same as heat removal in 30C. In the cycle shown, the gas is cooled from 120C 40C at constant pressure 100 bar in the heat exchanger, described as the cooler gas, Liquid formation occurs only when the extension to the lower levels of pressure. Will probably work system designed for transcritical operation in the subcritical regime, i.e. in the form of water vapor compression cycle at low temperatures and in this case gas cooler capacitor.
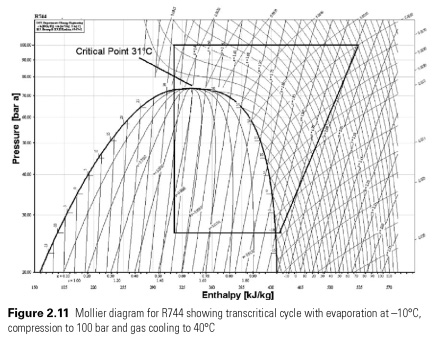
High pressure control is required for transcritical cycle. Optimal pressure is defined as a function of temperature at the outlet of the gas cooler and the balance between highest achievable cooling capacity and the lowest number of compressor energy.....
|

