The Greenhouse Effect (Global Warming)
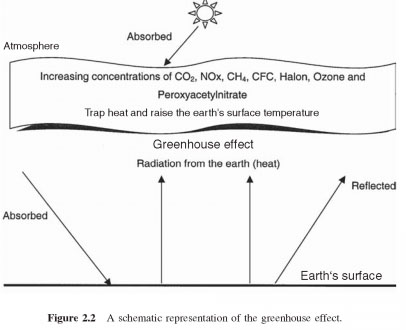
Although, the term " greenhouse effect was generally used for the role of the atmosphere (mainly water vapor and clouds) under the surface of the earth warmth, it was connected with that of CO2 (currently it is believed that CO2 is about 50% of the anthropogenic greenhouse effect). However, several other gases such as CH4, CFCs, halons, N2O, ozone, and peroxyacetylnitrate (so-called greenhouse gases) production of industrial and economic activities can also contribute to this effect, resulting in increased land temperature. Diagrammatic representation of this global problem is illustrated in Fig. 2.2.
The greenhouse effect of the phenomenon, the rays of the sun to the earth and maintain an average temperature of around +15 C. most of the infrared radiation reflected from the earth fell into CO2, H2O, and other substances (including CFCs), present in the atmosphere and kept going back to space. The increase in the greenhouse effect would lead to a sharp increase in temperature and it is very likely linked to human activities, in particular, emissions from fossil fuels.
In addition, the increase of the greenhouse effect may result in the following (Dincer, 2003):
- interim warming of the atmosphere (estimated at 3 to 5 C by 2050),
- increase of a level of oceans (estimated 20 cm by 2050), and
- climatic effects (droughts, rain, snow, heating, cooling).
increases in atmospheric concentrations of CFCs for about 24% of the direct increase in radiative heating of greenhouse gases over the last decade.
However, the observed decrease in stratospheric ozone, thought to be associated with the increase in stratospheric chlorine from CFCs, gives a negative radiative heating or cooling trend over the past decade.
Emission of CFCs in the atmosphere affects the climate in two ways (Badr et al., 1990):
- CFCs are extremely harmful greenhouse gas emissions (relative to CO2), because of their stronger IR range of intensities, stronger absorption features and long life in the atmosphere.
- CFCs to the depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer, which affects the temperature of the surface of the earth in two ways: more solar radiation reaching the surface of the lower troposphere system, resulting in a warmer climate and leads to a decrease in the temperature of the stratosphere and thus less infrared radiation, passed on the surface of the earth-lower troposphere system, resulting in lower surface temperature.
Thus, the net effect depends on the altitudes where the ozone changes happen...
|

