Global warming potential
Global warming is perhaps the most serious environmental issues facing civilization today. The risk associated with its consequences is described in terms of ecological disaster due to huge future climate changes. Global warming is the increase in global temperatures, which results in melting of polar ice caps and rising sea levels. It is connected with emission of so-called greenhouse gases that form a blanket and reflects the heat back to the earth's surface, or to retain heat in the atmosphere. The most notorious greenhouse gases carbon dioxide (CO2), which after the publication remains in the atmosphere for 500 years, so there is a constant increase over time progresses. The exact extent of the contribution due to human activities, may be uncertain, but in any case, it is important to keep it to a minimum and keep the stocks of fossil fuels, i.e., to minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
The main cause of CO2 emissions in the generation of electricity at power stations.
CO2 emission factor (kg CO2 per kWh electricity delivered) depends on the UK fuel mix for electricity generation. For coal-fired power stations, the figure is quite high, gas stations, below, and for hydro power, wind energy or nuclear power stations zero.
Electricity suppliers may require different mixtures generation type and, therefore, different emission factors, but the best currently available in the UK the average figure 0.422kg CO2/kWh (TEWI Guidelines IOR/BRA). This value is the average of the forecasts for 2005 and 2010. It is estimated that compressors for refrigeration in the UK consume 12.5 billion kW / h a year.
Global warming potential (GWP) of gas can be defined as an index comparing the climate impact of its issuing, uttering the same amount of carbon dioxide. The overall effect for a fixed time allows the collapse of the substance. The time horizon of 100 years is generally accepted, although this is much less than the lifetime of CO2 in the atmosphere. Refrigerant only to the impact of global warming if released into the atmosphere.
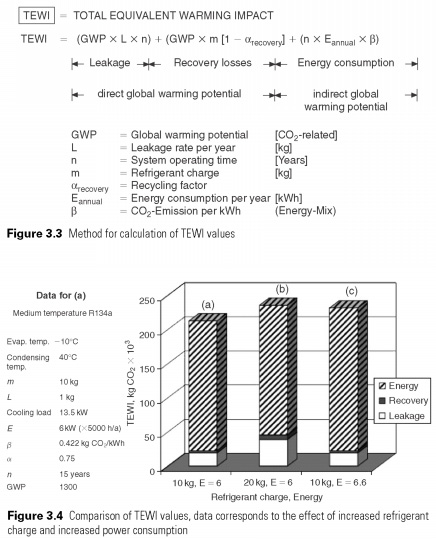
GWP values for HFC refrigerants can be seen in the Table. 3.1 R134a, for example, has a GWP of 1300, which means that the emission of 1 kg of R134a is equivalent to 1300 kg CO2 refrigerant choice affects the life of a warming impact system and the term total equivalent warming impact (TEWI) is used to describe the overall impact. It includes the effects of leakage of refrigerant recovery of refrigerant losses and energy consumption. TEWI should be calculated when comparing the system design parameters for specific applications. Complex method of calculation details, examples are given in the Guide. Figures 3.3 and 3.4 show the equation and an example for the average temperature R134a installation.
The largest element of the TEWI for the vast majority of refrigeration and air conditioning system is energy consumption. On Fig. 3.4 shows the dominant influence on the energy consumption of an element, which will increase by 10% and has a similar effect of doubling the amount of refrigerant leakage. Column (a) shows the original data, with the effect of a double charge and 10%growth in energy consumption in columns (b) and (c), respectively. The smaller the amount of energy required for the production of each kW of cooling the lower will be the effect on global warming.
 .... ....
|

 ....
....